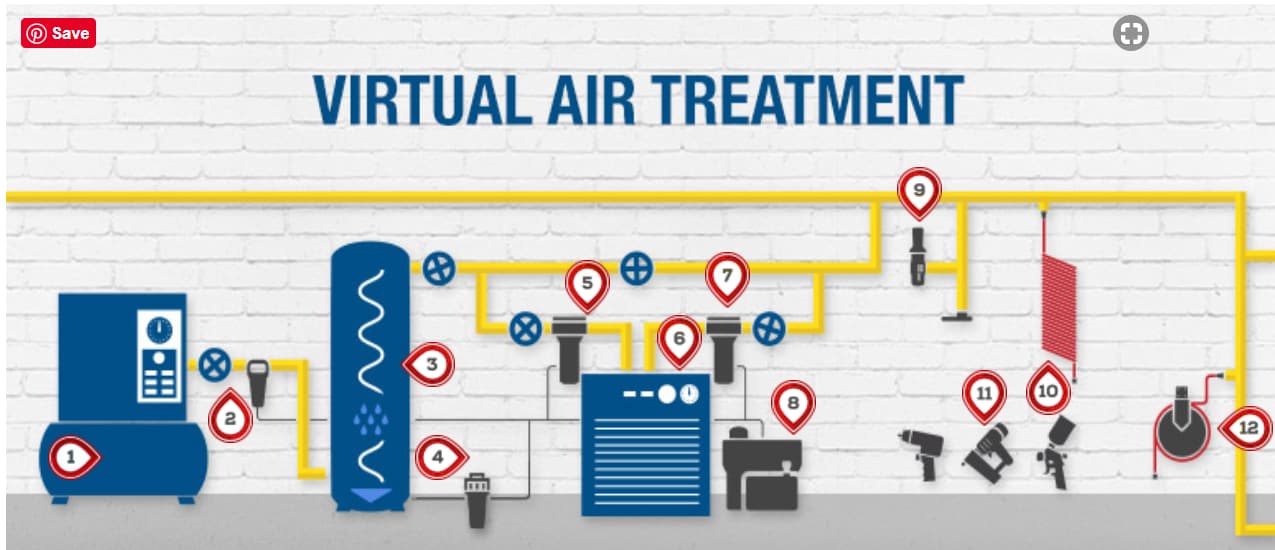
Compressed air is an essential component of many industrial and commercial processes, but it’s important to understand the importance of treating the air before use. Unfiltered and untreated air can contain moisture, dust, oil, and other contaminants that can damage equipment and lead to costly repairs or downtime. Compressed air treatment is a crucial step in maintaining the quality of air used in a variety of applications.
In this guide, we’ll cover the basics of air treatment, including what it is, why it’s important, and the various types of equipment used for compressed air treatment.
What Is Compressed Air Treatment?
Contents
Compressed air treatment is the process of removing impurities from compressed air before it’s used in industrial processes. The goal of air treatment is to ensure that the air is free from contaminants, so it won’t damage down-stream equipment or affect the quality of the product.
Compressed air treatment typically includes filtering, drying, and other processes to remove impurities and stabilize the air pressure. Depending on the application, air treatment can also include oil and other lubricants to reduce friction and improve performance.
Why Is Compressed Air Treatment Important?
Compressed air treatment is important because it helps ensure the quality of the air used in industrial processes. Without air treatment, the air can become contaminated with dust, moisture, and other impurities that can damage equipment and reduce product quality.
In addition, compressed air treatment is important for safety. Contaminated air can increase the risk of fire and explosions, and it can create hazardous working conditions for employees.
Types of Compressed Air Treatment Equipment
1. Filters: Filters are used to remove dust and other particles from the air. There are several different types of filters, including coalescing and particulate filters, as well as filter housings and filter elements.
2. Dryers: Dryers are used to remove moisture from the air. There are several different types of dryers, including desiccant, refrigerated, and membrane dryers.
3. Separators: Separators are used to remove oil and other lubricants from the air. They are typically used in applications that require the air to be free of oil.
4. Regulators: Regulators are used to maintain a consistent air pressure. They are typically used in applications that require the air to be delivered at a specific pressure.
5. Lubricators: Lubricators are used to add oil and other lubricants to the air. They are typically used in applications that require lubrication to reduce friction and improve performance.
Conclusion
Compressed air treatment is an essential step in maintaining the quality of air used in a variety of applications. By understanding the basics of air treatment, including what it is, why it’s important, and the various types of equipment used for compressed air treatment, you can ensure that the air used in your industrial processes is free from contaminants and safe for use.